T-7

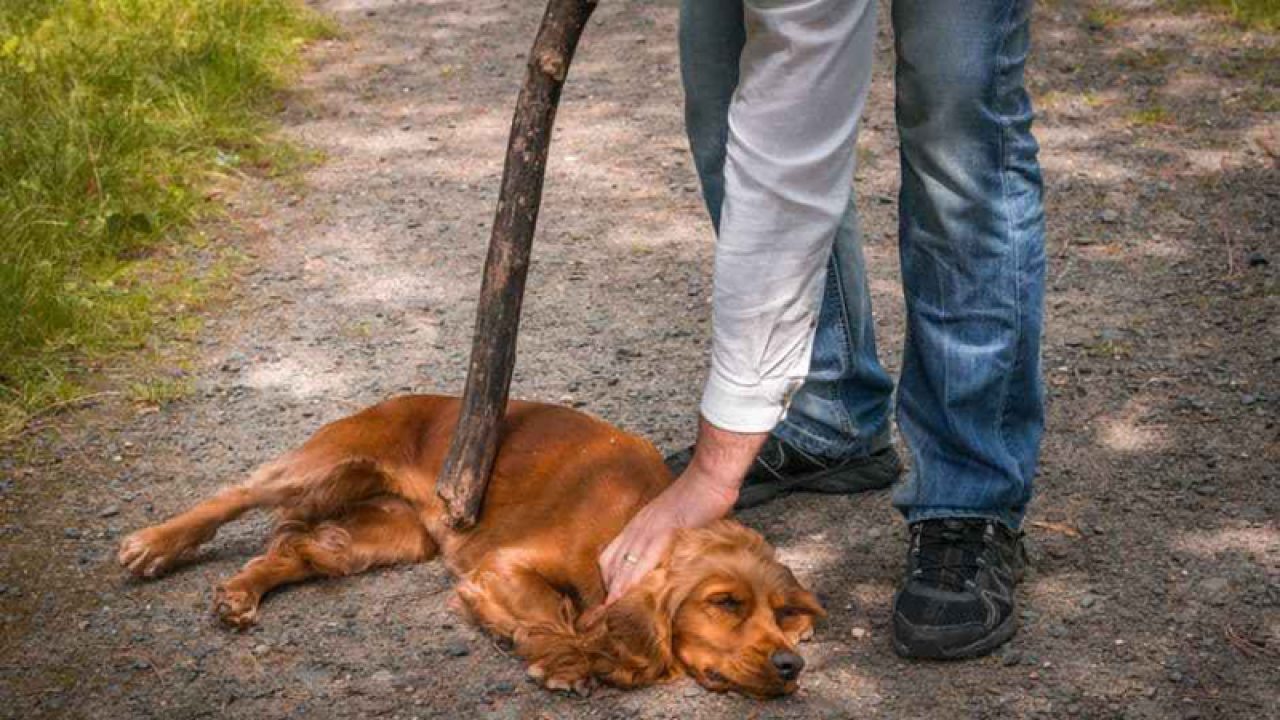
In a developing countries like India, China etc., animal abuse is very usual. For example, animals are used as a prop in circus ,even some people who owns a pet for entertainment and even in dairy farming animals are mistreated for increased milk yield. Every animal deserves to be treated right with value. To ensure the animal rights and in order to stop animal cruelty and to thrive these animals, Govt. of India passed Prevention of Cruelty Act, 1960.
PREVENTION OF CRUELTY TO ANIMALS, 1960
It defines the animals and different forms of animals (Domestic, Captive, Performing Animals) and enshrines the provision relating to the establishment of Animal Welfare Board, its functioning, power and regulatory under bodies. It provides certain guidelines relating to experimentation for scientific purpose along with it also discuss different forms of cruelty, exceptions and killing and suffering of the animal. In case of suffering and killing of a animal, it commits to relive it from the discomfort and put fine or imprisons the culprit.Cruelty in General – According of Section 11 of this Act, the following acts by any person are to be considered as cruelty :-
- Beating, Kicking, Runs over, Drives over, Tortures or otherwise treats any animal by unnecessary pain or suffering or any employment for such animals.
- employs animal in work or labor which due to any disease, infirmity, wound or any other cause
- Willful and unreasonable administration of any injurious drug or substance to any domestic or captive animal.
- Cages and confines any animal or other receptacle having insufficient growth in length and breadth permitting the animal a reasonable opportunity to move around
- keeping any animal chained or tethered by means of an unreasonable short or long chain for unreasonable time period
- being the owner of any captive animal fails to supply it with adequate food, drink or shelter
- Abandoning any animal in such situations causing it to suffer pain by reason of starvation or thirst, without any reason.
- Offering for sale or possessing any animal which is suffering pain, distress due to mutilation, starvation, thirst, over crowding or other ill-treatment
- For business purpose – organizes, keeps, management of any place for animal fighting or purporting to bait any animal or permits or offer place to be used or receives money for the admission of any other person to any place kept or used for any such purpose; or
- promotes or participates in any shooting match or competition where captive animals are released for the purpose of such an event.
They shall be punished, in case of a first offense, with a fine extending up to 50 INR, and in case of second or subsequent offence committed within 3 years of previous offence, with a fine of 100 INR, or imprisonment for a term which can be extend to 3 months or more.
However the following acts are excluded from the ambit of cruelty: –
- the training of animals for bonafide military or police purpose or exhibition of any animals so trained
- Any animal kept in zoological garden or by any society or association which for its principal object the exhibition of animals for educational or scientific purpose.
- Dehorning/Castration/Branding/Nose-roping of any animal if done in a prescribed method.

Captive Animal
Section 12 – Penalty for Practicing Phooka or Doom Dev – If any person practice phooka on any cow or milch animal to improve lactation which is injurious to the health of animal or permits such operations being performed upon such animal in his possession or under his control, he shall be punishable with a fine which may extend to 1000 INR or with imprisonment for a term which may extend to a term of 2 years or with both, and the animal on which the operation was performed shall be forfeited to the Government. It is Cognizable Offence.
Section 13 – Killing of Suffering Animal – This provision relating to the killing of an animal so as to relieve it from any further suffering. This section is implemented by the order of Court. when the court decides it is cruel to keep the animal alive to direct that the animal be destroyed and to assign the animals to any suitable person for that purpose, and the person to whom such animal is so assigned shall as soon as possible, destroy such animal or cause such animal to be destroyed in his presence without unnecessary suffering.No order shall be made under this section except upon the evidence of a veterinary officer in charge of the area.
Experimentation of Animals – Chapter – IV – According to this Act, nothing shall affect the experimentation (including operation) on the animal for the purpose of Advancement through the new discovery of physiological knowledge, knowledge useful for decreasing the mortality rate, combating disease, suffering alleviation. Experimentation is guarded under Section 14 of the Act. Committee for controlling and supervising experiments on animal is constituted under the Section 15 of this Act. Committee’s fund shall include governments grants provided to it time and again along with the following made to the by any person –
- Contribution
- Donation
- Subscription
- Gifts

Using Animals for Performance
Performing Animal
Exhibition and Training – Section 21 – It refers to exhibit at any entertainment to which public makes admission through purchasing of tickets and training means to train any animals for the purpose of such exhibition, and the term exhibitor and trainer has a corresponding meaning
.Section 22 – Puts Restriction on exhibiting performing Animals and Section – 24 gives Judicial Power to prohibit or restrict exhibition or training. Section 25 grants powers to any person authorized by the prescribed authority in writing and any Police Officer, not below the rank of Sub-inspector to enter the premises.Section 26 – Offence in relation to the Performing Animal
Exemptions – Section 27
Treatment and Care Section 35 of this Act, The state government may appoint infirmaries for the treatment and care of the animals in respect of which offences under this Act have been committed, and may authorize the detention of any animal which requires its production before the magistrate.
For complete reading of the Prevention of Cruelty to Animal Act, 1960, Check the links below. http://www.awbi.in/policy_acts_rules.html
http://www.awbi.org/awbi-pdf/APL.pdf
” I believe animals should be respected as citizens of this earth. They should have the right to their own freedom, their own families, and their own life.” If you see any kind of animal cruelty around you, do not neglect it but report it using PCA -1960 to the nearest Police Station, Animal Organizations.
THE GEEK VETERINARIAN